Blog
Gastroparesis Symptoms, Diet Tips, and Healing
Gastroparesis Symptoms, Diet Tips, and Healing Foods That Help
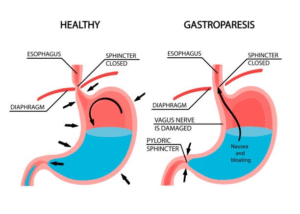
What Is Gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis is a chronic digestive condition where the stomach takes too long to empty its contents. This delay can cause uncomfortable Gastroparesis symptoms such as nausea, bloating, early satiety, and abdominal pain. People with this condition often struggle to maintain proper nutrition and hydration. Managing gastroparesis involves more than just medication—it requires mindful eating habits and strategic food choices. Following personalized diet tips like eating small, frequent meals and choosing easily digestible, low-fat foods can help ease symptoms. While there is no cure, many individuals find relief and improved quality of life through dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes that support healing.
-
Definition in simple terms
-
What happens in the body
-
Who is most affected
-
Link to Mayo Clinic Gastroparesis Overview (external)
Common Symptoms of Gastroparesis
-
Nausea and bloating
-
Feeling full quickly
-
Vomiting undigested food
-
Abdominal pain
-
Poor appetite and weight loss
-
Importance of tracking symptoms (Download our free symptom tracker) if you purchase our 25 Gastroparesis Simple Recipes for Sensitive Stomachs eBook.
Causes and Risk Factors
-
Diabetes-related gastroparesis
-
Post-surgery complications
-
Medication side effects
-
Neurological conditions
-
Idiopathic cases (unknown cause)
Diagnosing Gastroparesis
-
Gastric emptying study
-
Upper endoscopy
-
SmartPill test
-
Importance of medical support
Diet and Lifestyle Tips That Help
-
Eat small, frequent meals
-
Focus on low-fat, low-fiber foods
-
Sit upright after meals
-
Avoid carbonated drinks and raw vegetables
-
Keep a Gastroparesis Food Journal)
Healing Foods for Sensitive Stomachs
-
Banana and rice porridge
-
Mashed sweet potato
-
Blended vegetable soups
-
Bone broth and pureed chicken (if not vegetarian)
-
Herbal teas (ginger, peppermint in moderation)
H3: Foods to Avoid
-
High-fiber raw fruits/veggies
-
Fried or fatty foods
-
Tough meats
-
Beans, lentils, and whole grains
-
Caffeinated and carbonated drinks
When to Seek Medical Attention
-
Persistent vomiting
-
Severe weight loss
-
Signs of malnutrition
-
Medication review with your doctor
Final Thoughts: Managing Gastroparesis Day by Day
-
Patience and consistency are key
-
Customize your diet
-
Use tools like journals and meal plans
